One of our library working groups has been working for some time on the mapping of Citizen Science projects in Hungary and Europe, with particular interest on Pécs of course.
In connection with this, we are starting a series of blogs entitled “Link to knowledge”, serving as a framework of our work, while trying to present as many projects as possible through interviews, as well as offer a place to learn about the concept and possibilities of Citizen Science.
In our first article, we present the idea of Citizen Science and the current activities of our working group.
Benefits of Citizen Science in our Community
In Hungary, Citizen Science is mostly used for data collection, crowdsourcing or mapping of natural areas, but Citizen Science is more than that. In a world branded by fake news, misinterpretations, declining attention to professionally qualified expert, and the diminishing respect for professionally trained researchers, we see Citizen Science become more and more interesting and valuable.
The Role of Science
Science has an impact on a wide range of our private and social life as it serves as one of the key factors in political, economic and personal developments and decisions. By furnishing new insights, technologies and ways of thinking about our world, science has the potential to change and elevate society. At the same time, it also systematically tests its own results, methods and premises. Today science is characterised by an ever-increasing complexity through the vast fields of specialisations, thus becoming increasingly difficult for many people to evaluate its opportunities and recognise its possible conflicts. While some citizens feel disconnected from this process, others are busy developing an advanced and new critical attitude towards science. More and more people increasingly see themselves not only as its beneficiaries but also as participants in it as they fight for more influence. Social media provide them with effective tools for doing so whether it is in the form of blogs, discussion forums, citizens’ initiatives or Citizen Science projects. These also provide diverse sources of information – as well as often contradictory results and conclusions to manage and solve.
The Role of the Community
Citizens can advance or hinder science, decide to place their trust in it or not, thus, reliable information from and about the realm of science is becoming ever more important. Equally great is the responsibility raised by the various stakeholders involved in science communication. The frameworks have changed, and not only due to developments within science and society, but on the account of dwindling resources, traditional journalism is becoming less able to critically evaluate the reliability of information. At the same time, science PR has more opportunities than ever to reach citizens directly on the internet, through social media or through events and exhibitions. This also rises the expectations regarding the accessibility and quality of the information and the services it provides.
Citizen Science is an integral part of the Open Science ecosystem. The active involvement of society in the collection of data and information through methods of crowdsourcing is an internationally accepted approach that contributes to a more open and easily accessible state of science. It is essential that all Citizen Science projects continue to focus on the acquisition of scientific knowledge.
How we started?
The project team operating in the University of Pécs Library was created in 2021 with the aim of mapping and supporting scientific projects related to the University of Pécs and those affecting the community. We consider our priority to provide services that can increase the direct social impact of the knowledge and results generated at the University. Highly successful scientific educational events and lectures were already a common practice at the university; however, our intention is to involve and develop an active community based on dialogue, cooperation with society and feedback from the academic life of the university. Thus, the University Library fills the role of a bridge between knowledge and society and continues to serve as a threshold.
Our goal is to create a cultural, scientific and community-driven network that can be an attractive and open meeting space for instructors who are able and willing to transfer knowledge, and students and citizens who are receptive to knowledge and values, so that they can cooperate and mutually increase each other’s worldview.
Where are we now?
The project team is currently working on mapping the projects operating at the university or involving and cooperating with communities directly connected to the university.
Even though the initiative is still in its infancy, it has already begun to form the initial network of Citizen Science projects.
In the future, we will try to build a model of Citizen Science, a model that places great emphasis on partnerships. The fact that this attitude is not alien to the researchers of the University of Pécs and that the practice of dialogue between science and community have already appeared in several initiatives is encouraging. We hope that these projects will not only serve as an example for the inclusion of new knowledge and methods in other projects but will also give birth to new independent initiatives.
In order to archive this, the library has decided to collect and represent the current and past Citizen Science projects of the university.

Get to know UP’s projects, for which you can even submit data today, participating and helping their work!
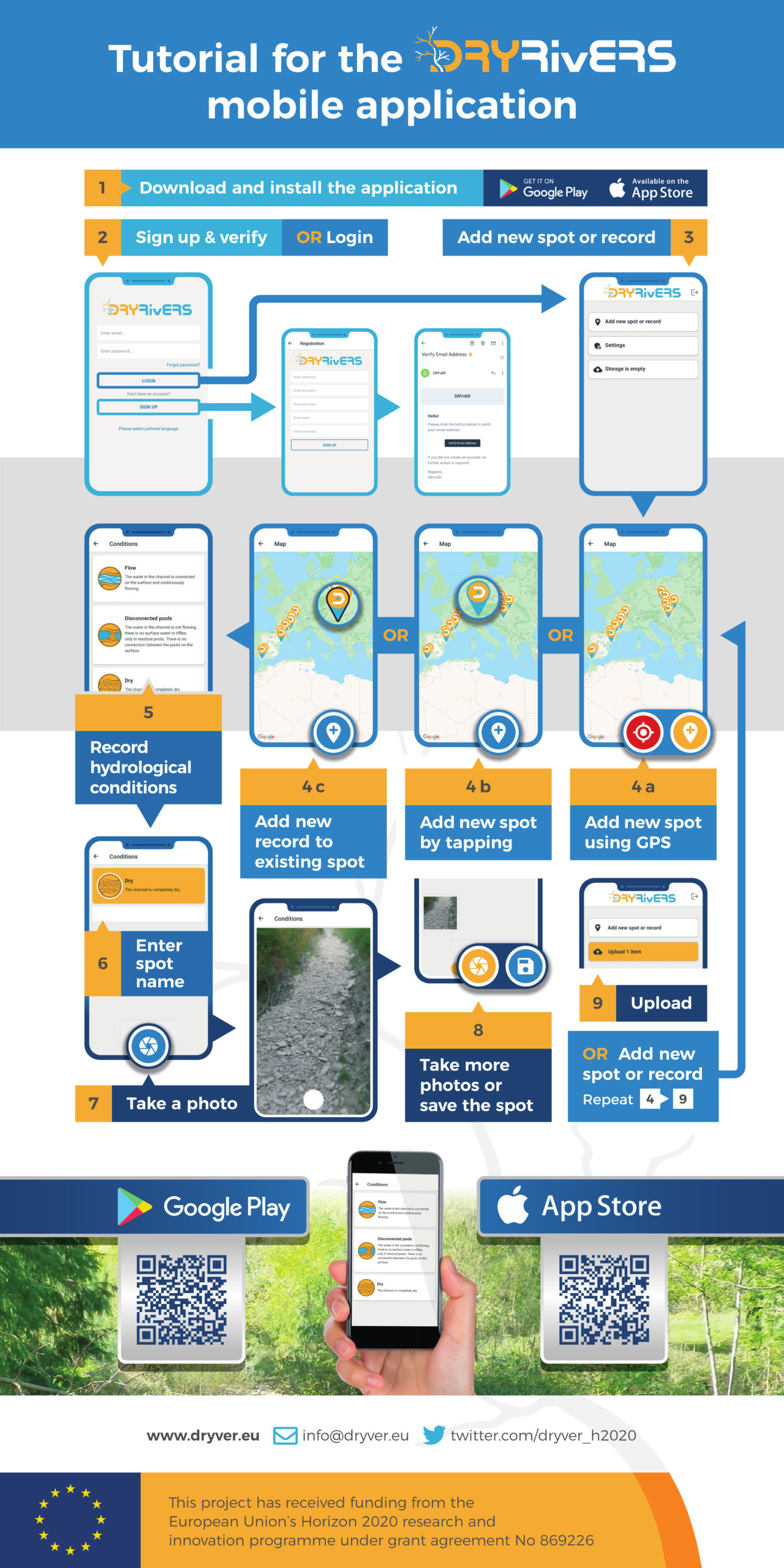
DRYvER
Rivers, streams, lakes, and wetlands are among the most valuable, not to mention the most fragile ecosystems on Earth. These habitats are crucial for future of economy and for human survival as well. However, rivers and streams are threatened by climate change and increased human water use, which cause them to dry up, and the percentage of drying channels in river networks are also dramatically increasing worldwide, including in Europe. Because shifts from permanent to intermittent flow regimes represent major tipping points for rivers, with often irreversible environmental and societal consequences.
DRYvER aims to collect, analyse and model data from nine DRNs in Europe and South America to create a novel global meta-system approach that incorporates hydrology, socio-economics, ecology and biogeochemistry in order to craft strategies, tools and recommendations for adaptive management of river networks.
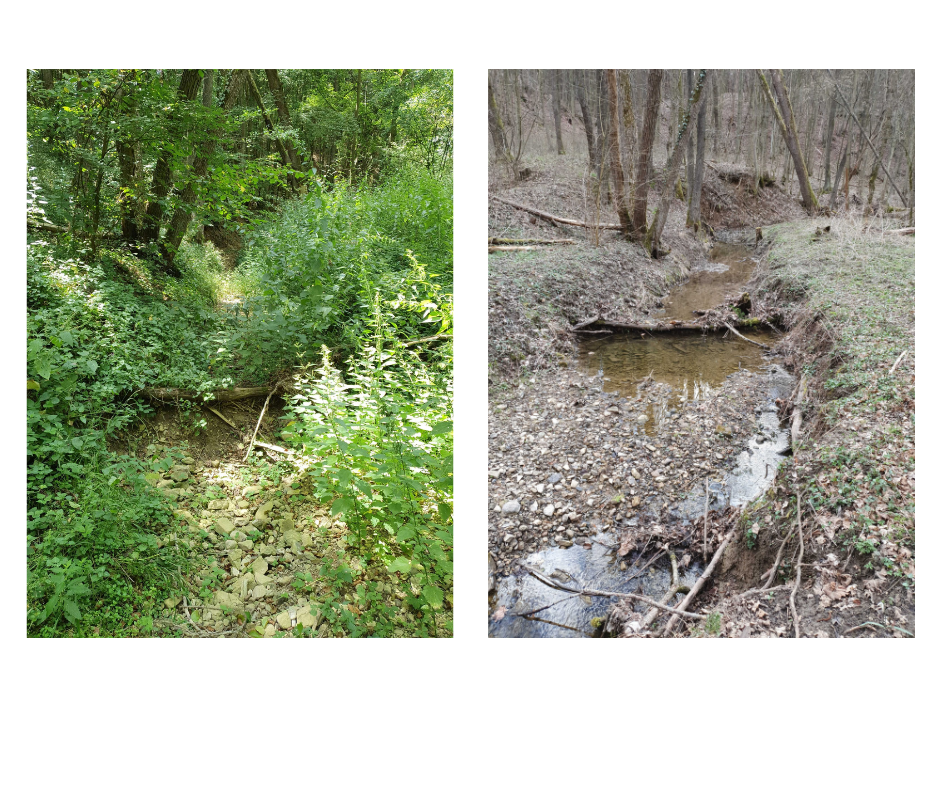

Working in collaboration with resource managers and citizens, the DRYvER team plans to co-develop new strategies to mitigate and adapt to the effects of climate change on these networks.
For more information check these websites:
Mosquito Alert
Mosquito Alert is a non-profit cooperative Citizen Science project, coordinated by different public research centres including the University of Pécs. The goal is to study, monitor, and fight the spread of invasive mosquitoes capable of transmitting global diseases.
Due to climate change, as well as significant increase in international trade and tourism, consist of the main cause behind the emergence of new, tropical species in Europe. Invasive mosquito species are potential vectors of several pathogens posing a dangerous risk to both humans and domestic animals as well. In order to understand the epidemiological threat, we need to know the spatial and temporal distribution patterns of these species. For this purpose, researchers of the Ecological Research Center and the University of Pécs launched a mosquito monitoring program (szunyogmonitor.hu) covering the entire country in 2019 with the involvement of the population.
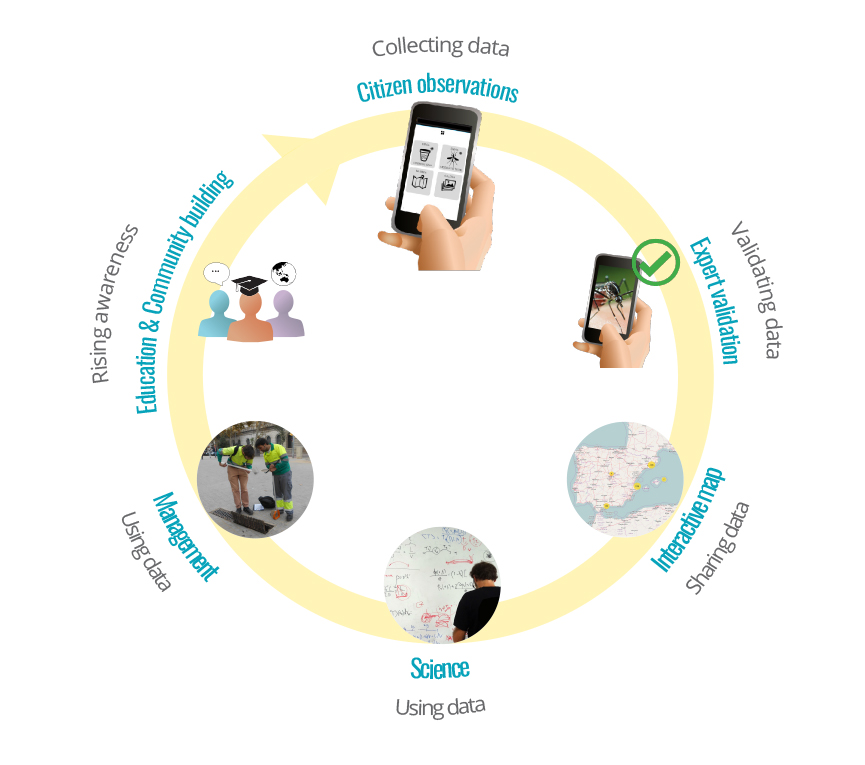
Surveillance is carried out with the Mosquito Alert app, which allows anyone to notify, by means of a photo, the possible discovery of one of the mosquitoes studied, as well as that of their breeding places in public spaces. Along with the photo the location of the observation and other necessary information to help in the identification of the species are collected. A human team of expert entomologists is in charge of validating the photos received and notifying the participant of the result. The scientific conclusions derived from the data obtained with the participation of society will enable the planning of targeted on-site sampling, the good allocation of resources, and the preparation for a possible epidemic through the detection of pathogens in the collected mosquitoes.
For more information check these websites:
The app is available on the Google Play Store and the App Store.

Our future…
According to the third mission of the University of Pécs strategy, the aim of our activity is:
- Supporting academic and research progress;
- Encouraging independence, action and cooperation;
- Strengthening the service functions of higher education, both towards students and the local society;
- Expanding the range of customizable digital content services;
- Contributing the innovative, scientific and cultural activities in the region;
- Promoting the democratization of science and the desire for knowledge created at the university through open access.
For more information visit our website.
If you have a Citizen Science project that you would like to present to us or have questions about how to host your Citizen Science project, or how to participate please contact us.
Molnár Dávid: molnar.david@lib.pte.hu
Szemes-Révész Enikő: revesz.eniko@lib.pte.hu


Leave a Reply